# Entando Local Hub
The Entando Local Hub is a repository for modular components directly accessible from an Entando App Builder. Entando Bundles catalogued in the Local Hub can be deployed, installed, and updated with a few clicks of a button, to be employed in any application.
Details of the Local Hub are examined below.
# Entando Component
Entando defines a component as an identifiable resource, a block of code or a grouping of related code blocks that can be used independently in an Entando Application. Examples of components are widgets, plugins, micro frontends, microservices, packaged business capabilitities, content types, labels, plugins, and static resources.
# Entando Bundle
An Entando Bundle is a package containing one or more components, the required descriptor files, and bundle metadata.
A git-based bundle requires a descriptor.yaml and is published in a Git registry. A docker-based bundle requires an entando.json and is published to Docker. Both docker-based and git-based bundles can be utilized in an Entando Application with the EntandoDeBundle custom resource, but docker-based bundles are recommended.
# EntandoDeBundle Custom Resource
The EntandoDeBundle custom resource is a Kubernetes resource read by the Entando Operator. It provides information about the bundle and makes it available to the Entando Component Manager in Kubernetes, making it accessible from the App Builder.
# Entando Component Manager
The Entando Component Manager is responsible for the installation and removal of components from the entando-core. It creates the connection between the EntandoApp
and the Kubernetes integration service, interacting with both the entando-core and the Kubernetes cluster and managing the communication between an application and the installed microservices.
# Entando Kubernetes Integration Service
The Entando Kubernetes integration service, or entando-k8S-service, is part of the Platform infrastructure and responsible for the low-level communication with the K8s cluster API. It reads the bundles in an Entando Cluster and serves them with an API accessible from the App Builder.
# Architecture
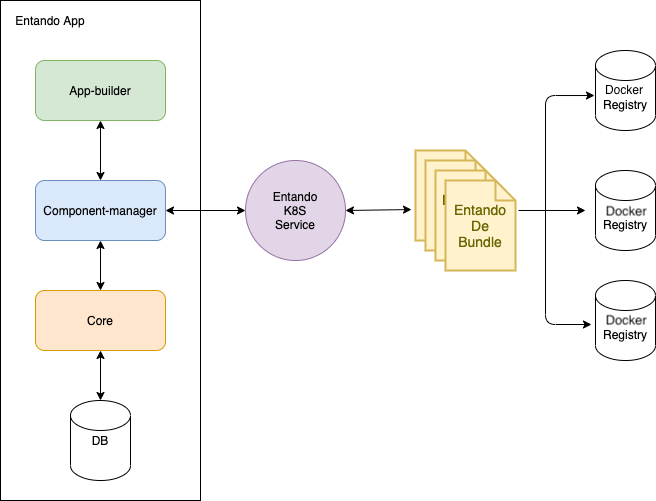
The following flow describes how the App Builder, Entando Kubernetes integration service and Component Manager interact to populate the Local Hub with bundles.
# Example Flow
The user navigates to the Hub page in the App Builder to view the bundles shared with the EntandoApp
The App Builder requests a list of bundles available to the EntandoApp from the Entando Component Manager
The Component Manager queries the
entando-k8S-serviceto retrieve the list of bundlesThe
entando-k8s-servicequeries the cluster/namespace(s) and returns the list of available bundles to the Component ManagerThe Entando Component Manager sends the list to the App Builder
The available bundles appear in the Hub page of the App Builder, where they can be installed and managed by the user