# Entando Multitenancy
# Overview
Starting with Entando 7.2, the Entando Platform includes support for multitenancy. An Entando Application can be customized to enable a multitenant architecture where tenants share an infrastructure but are informationally isolated. This document provides an overview of multitenancy and Entando's implementation.
# Core Concepts
Multitenancy describes an architecture in which a single software instance serves multiple tenants. Each tenant, identified by a unique domain name, comprises a user group with specific access privileges to the instance. A multitenant software application is designed to provide a common architecture while ensuring the segregation of information between tenants.
Entando Multitenancy imposes a shared architecture (the versions of Entando, K8s and Keycloak) while distributing resources (CPU, memory) across the primary and secondary tenants. The primary tenant refers to the user group with full access to the default features and functionalities of an Entando instance. Secondary tenants comprise user groups who share certain privileges and capabilities of the primary tenant.
Note: Access to the Local Hub and installation of bundles from a Hub catalog is restricted to the primary tenant.
Each tenant is informationally isolated from the others with its own data, configuration settings, and user management. Kubernetes Secrets are used to protect the confidential parameters of tenant configurations.
# Architecture
All tenants rely on a single instance of an Entando Application for core functionality such as the App Builder, App Engine, and Keycloak.
Redis is necessary for cache management and high availability, which Entando strongly recommends for a multitenant configuration. See the Redis Integration tutorial to add it to your Entando Application.
Tenants are differentiated by unique domain names. To isolate its information and configurations, a tenant is allocated one each of the following:
- A database or schema for independent data storage
- An Entando Content Delivery Server (CDS) instance to manage static resources external to the Entando App Engine
- A Solr core to implement an external search engine
- A Keycloak client realm to manage user access
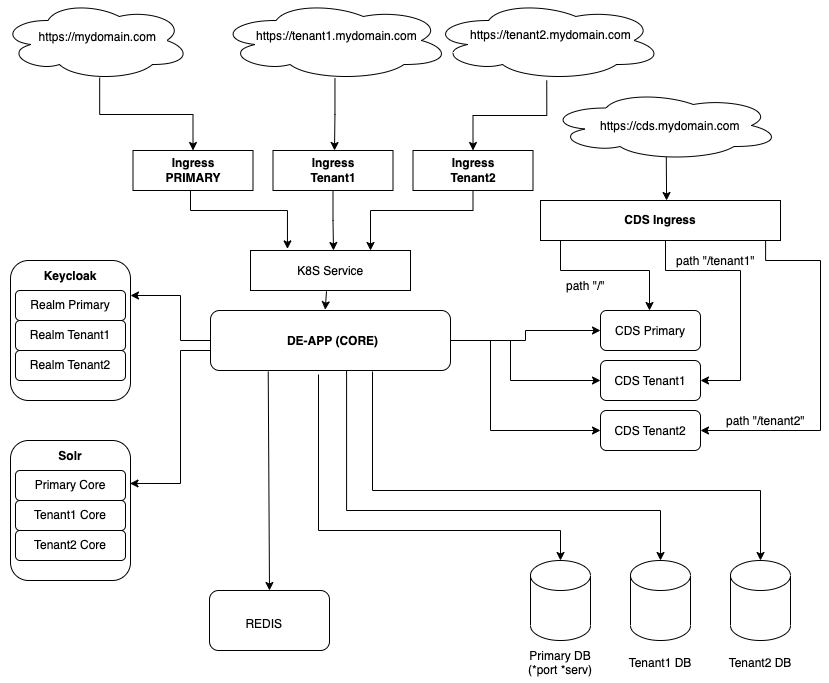
Entando Multitenancy requires that Solr, Entando CDS, and Keycloak are configured for each tenant.
# Implementation
A single installation of Entando can manage more than one independent and isolated site. While secondary tenant sites are dynamic and content-driven, their composability is limited. The following are key features of Entando Multitenancy:
- The domain name in the URL of the Entando instance identifies the current tenant
- Separate databases (or schemas) and filesystems physically isolate each tenant's data
- Different security domains (users, keys) hosted on different Keycloak realms ensures that each tenant's activity is independent
- Each multitenant configuration relies on a single Kubernetes namespace, Entando App Engine, and Entando App Builder
- The App Builder UI of the primary tenant is indistinguishable from that of a standalone Entando installation
- Aside from the hidden "Hub" and "EPC" menu items, the App Builder UI of a secondary tenant is indistinguishable from that of a standalone Entando installation
# Next Steps
Start here to configure Multitenancy on Entando.