# Entando Bundle
The structure of an Entando Bundle leverages composable development methods, decoupling microservices, micro frontends, API management, and services such as databases. The ent bundle CLI module administers the process, using the descriptor entando.json. This single bundle descriptor defines all the components and resources of the docker-based bundle. The following page describes the descriptor, the structure, its conventions, and the building process.
The docker-based approach is an improvement on the previous Entando Bundle structure and to see the differences, refer to the Bundle Evolution page.
# Entando Bundle Conventions
- There is a single bundle descriptor,
entando.json, initialized and managed by the ent bundle CLI. - Microservices and micro frontends can be built independently, each with their own folders.
- The
platformdirectory is dedicated to platform specific components such as fragments, pages, and static resources. For more information on component types and descriptors, see the Bundle Component Details page. - The
svcdirectory is allocated for auxiliary services and the docker-compose configuration files that define them. The ent bundle module enables, starts and stops the services. MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Keycloak services are available with Entando out of the box, and for more details, go to the ent CLI Services page. - Optionally, a thumbnail for your bundle can be set by adding a JPG or PNG image file to the bundle root folder. The file must be named "thumbnail" and be 100kb or less, e.g. thumbnail.png.
# Project Structure
bundle-project/
.git/
.entando/ <= An internal working folder for caches, logs, and build artifacts
config.json
output/
descriptors/
logs/
microservices/
microfrontends/
microservices/ <= Source and build output for each microservice
ms1/
ms2/
ms3/
microfrontends/ <= Source and build output for each microfrontend
mfe1/
mfe2/
mfe3/
mfe3-config
platform/ <= platform specific components
pageTemplates/
page-template.yaml
pages/
svc/ <= auxiliary services for local development
keycloak.yaml
...
entando.json <= project bundle descriptor
thumbnail.jpg <= bundle thumbnail
Note: For a full list of platform components, see the Bundle Component Descriptors page.
# Bundle Development Process
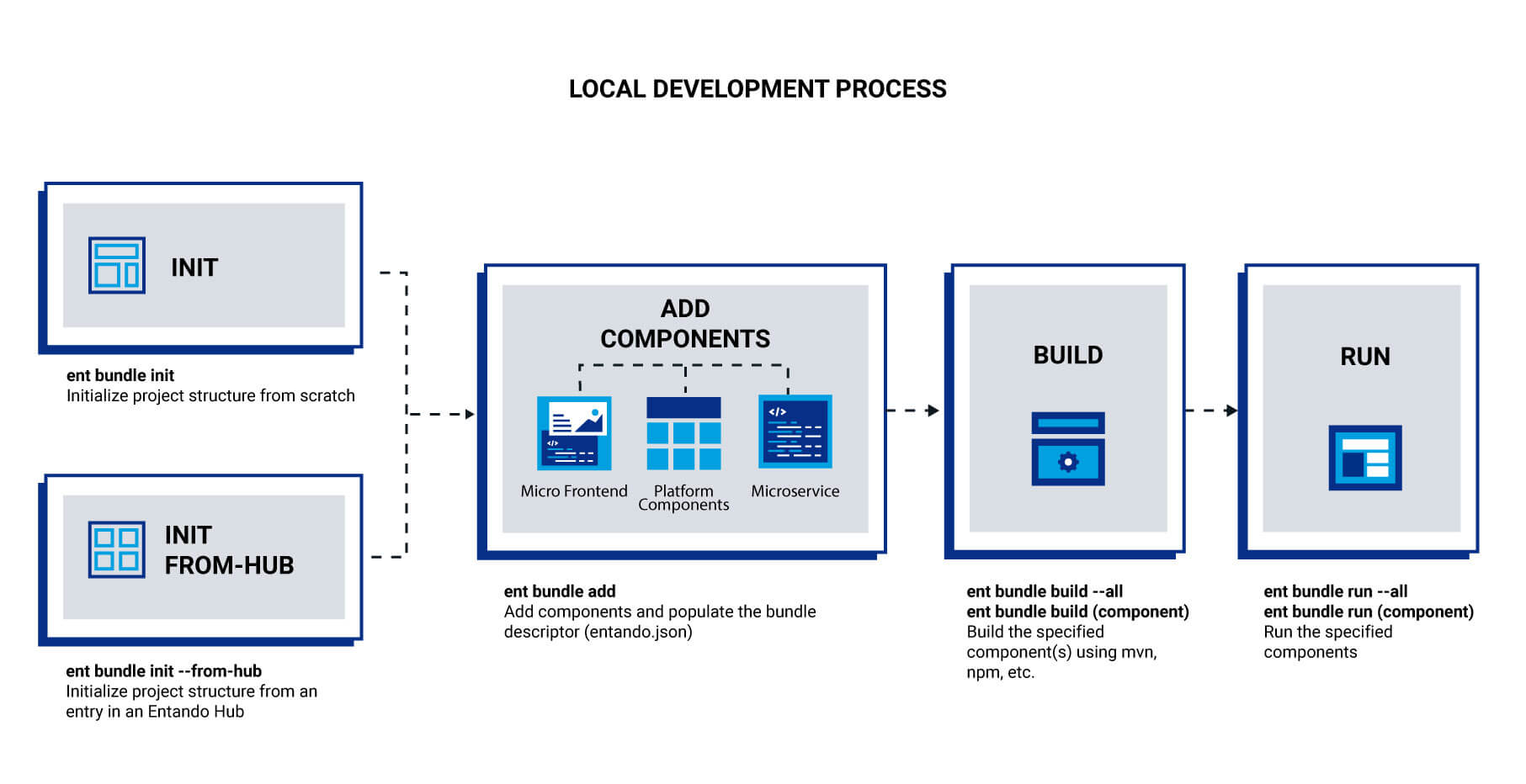
The ent bundle CLI module manages the building and publishing of an Entando Bundle. From initialization to installation, from adding MFEs and MSs to calling for services such as Keycloak and making API claims, the ent bundle commands streamline the development process.
At initialization, the project scaffolding is built. A project can be started from scratch with this structure or retrieved interactively from an Entando Hub as a starting point for new bundles. Microservices, micro frontends, components, services, and API claims can then be added. At this stage, components can be run locally and independently with the ent bundle commands.
The next steps build and pack the project using the bundle descriptor. The specifics depend on the component type and stack. The build phase constructs the microservices and micro frontends while the pack command generates the artifacts and Docker images. Images are built for the bundle and for each microservice.
In the publish step, images are pushed to a Docker registry and tagged according to the bundle configuration. A custom registry can also be used.
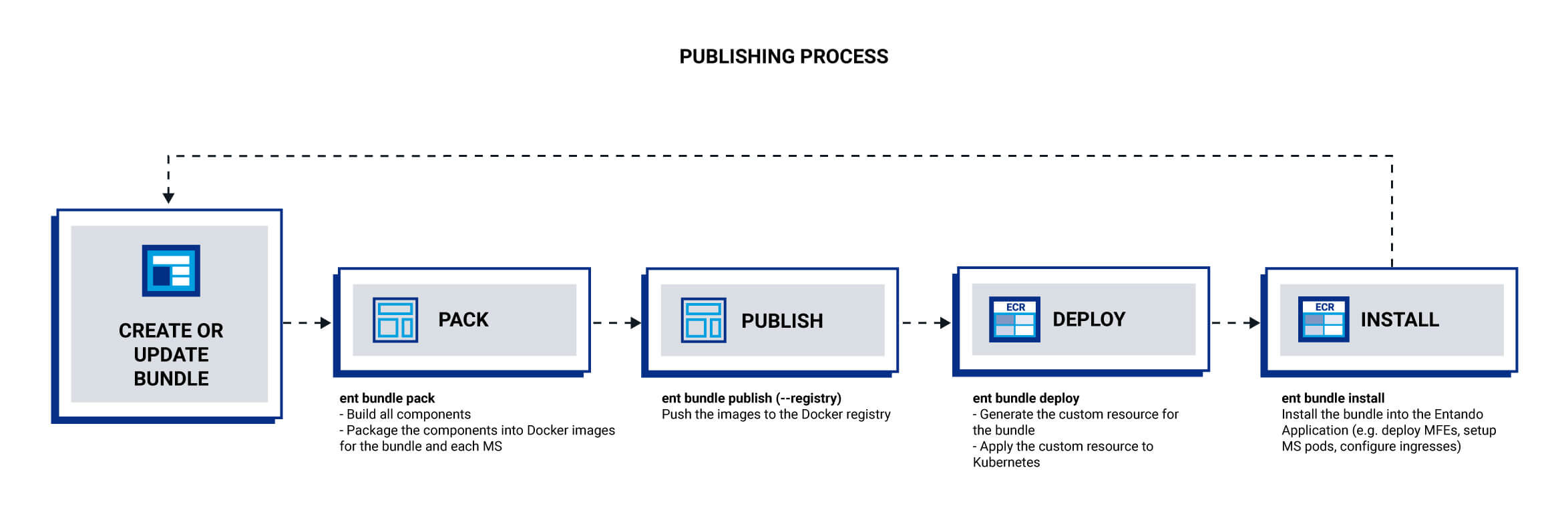
Finally, the bundle is deployed into the Local Hub of a running Entando instance where it can then be installed. Any improvements to the bundle can be made by repeating the four steps: pack, publish, deploy and install. Alternatively, the install step can be done in the App Builder UI by the composer designing the application.
At every phase of the process, options are available to fine-tune the process, and to see more information, go to the ent bundle CLI documentation.
# Bundle Descriptor entando.json
The following is a list of specifications for the bundle descriptor and its component parts.
# Bundle Descriptor Specifications
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | String | Yes | The bundle project name used as the default Docker image name |
description | String | No | A description of the bundle project shown in the App Builder |
version | String | Yes | The bundle version used as the default Docker image tag |
displayName | String | No | A descriptive label used in the UI in place of a name |
global | Global[] | No | Global bundle configuration items |
microservices | Microservices | No | Bundle microservices |
microfrontends | Micro Frontends | No | Bundle micro frontends |
{
"name": "my-bundle-name",
"description": "my bundle description",
"type" : "bundle",
"version": "0.0.1",
"svc": [
"keycloak"
]
}
# Microservices Specifications
| Name | Type | Required | Possible Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
name | String | Yes | Microservice name | |
stack | Enum | Yes | *spring-boot *node *custom | Microservice stack |
dbms | Enum | No | *none^ *embedded *postgresql *mysql | DBMS required by the MS to provide services |
healthCheckPath | String | No | Endpoint for a health check | |
ingressPath | String | No | Custom ingress path for health check | |
deploymentBaseName | String | No | Used to define custom pod names | |
permissions | Permission[] | No | List of permissions to grant to the microservice | |
roles | String[] | No | Exposed security roles | |
env | EnvironmentVariable[] | No | Required environment variables | |
| Microservices Environment Variables | No | Entando-provided env variables for MS | ||
commands | Command[] | No | Custom command(s) definitions | |
version | String | Required only for a custom stack | Microservice version override |
^ dbms none: Oracle and other DBMS types are not supported for automatic deployment in a container. Bundle env variables should be used instead, similar to connecting the EntandoApp to an external database.
# Microservices Sample Code
"microservices": [
{
"name": "my-ms",
"stack": "spring-boot",
"dbms": "mysql",
"healthCheckPath": "/management/health",
"ingressPath": "/ingress",
"roles": ["admin"],
"env": [
{ "name": "SIMPLE_VAR",
"value": "mySimpleValue"
},
{ "name": "SECRET_VAR",
"secretKeyRef": {
"name": "YOUR-BUNDLE-ID-my-secret",
"key": "mySecretKey"
}
}
]
}
]
# Microservices Details
Entando recommends that REST APIs be added to microservices.
To utilize environment variables, inline or based on Kubernetes Secrets, see the Plugin Environment Variables tutorial.
Entando uses the
healthCheckPathto monitor the health of the microservice. A plugin in an Entando Bundle can use any technology, as long as it provides a health check service configured via thehealthCheckPath. This path must be specified in the descriptor file and return an HTTP 200 or success status. This can be implemented by a Java service included with the Entando Blueprint in the Spring Boot application. You can also use a Node.js service as shown here (opens new window).
# Micro Frontends Specifications
| Name | Type | Required | Possible Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
name | String | Yes | Micro frontend name | |
stack | Enum | Yes | *react *angular *custom | MFE stack |
type | Enum | Yes | *widget *widget-config *app-builder | Type of MFE |
category | String | No | Default is User | For widget type only, any custom name (See below) |
slot | Enum | Yes for type=app-builder | *primary-header *primary-menu *content | Named reference to an App Builder embedded position in a specific layout |
paths | String[] | Yes for type=app-builder and slot=content | App Builder activation paths | |
titles | String[] | Yes for type=widget | Localized widget labels | |
group | String | Yes | Visibility group name | |
publicFolder | String | No | Default is public | MFE public folder (typically where index.html is located) |
apiClaims | String[] | No | See API Claim spec below | |
nav | MenuEntry[] | No | Bundle menu global links | |
commands | Command[] | No | Custom commands definitions | |
buildFolder | String | No | Default is build | Corresponds to the MFE build folder |
configMfe | String | No | The custom element for the corresponding widget-config MFE | |
params | MfeParam[] | Yes | User configuration for executing a widget | |
contextParams | String[] | Yes | Information extracted from the application context | |
version | String | Required only for custom stack MFE | Microfrontend version override |
# Configure a Path for Static Assets
To configure your micro frontend with access to static assets, Entando provides two paths, one for widgets and another for EPCs.
For widgets:
window.entando?.widgets['YOUR-MFE']?.basePath;For EPCs:
window.entando?.epc['YOUR-EPC']?.basePath;
See the instructions for setting the path in a React MFE.
# Custom Category
A custom category provides an organizing classification for Widgets, to appear as a separate grouping in the App Builder Page Designer. A custom category can only be used with MFEs of the type widget. All widgets or MFEs will appear under User Widgets unless a custom category is specified.
# Micro Frontends Sample Code
"microfrontends": [
{
"name": "my-mfe",
"stack": "react",
"titles": { "en": "My MFE Title", "it": "Il Mio Titolo MFE" },
"type": "app-builder",
"category" : "My custom category",
"slot": "content",
"paths": ["/path1"],
"group" : "free",
"apiClaims": [...]
},
{
"name": "my-mfe2",
"stack": "custom",
"type": "widget",
"publicFolder": "public",
"titles": { "en": "My MFE2 Title", "it": "Il Mio Titolo MFE2" },
"group": "free",
"commands": {
"build": "echo 'Please edit this command to customize the build phase' && exit 1",
"run": "echo 'Please edit this command to customize the run phase' && exit 1",
"pack": "echo 'Please edit this command to customize the pack phase' && exit 1"
},
"version": "0.0.1"
}
]
# API Claim Specification
| Name | Type | Required | Possible Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
name | String | Yes | Name | |
type | Enum | Yes | *internal *external | Category of claim, either inside the same bundle (internal) or same namespace (external) |
serviceName | String | Yes | The name of the microservice | |
serviceUrl | String | No | The URL of the microservice deployed in the local environment | |
bundle | String | Yes only for type=external | Bundle Docker URL |
# API Claim Spec Sample
"apiClaims": [
{
"name": "int-api-claim",
"type": "internal",
"serviceName": "my-ms"
},
{
"name": "ext-api-claim",
"type": "external",
"serviceName": "my-ext-bundle-ms",
"bundle": "registry.hub.docker.com/my-organization/my-ext-bundle-ms"
}
]
For more information, go to the API Management page.
# Command Specification
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
build | String | No | Custom build command |
run | String | No | Custom run command |
pack | String | No | Custom pack command |
# Command Spec Sample Code
"commands": {
"run": "mvn -Dspring-boot.run.arguments=\"--server.port=8082\" spring-boot:run"
}
Depending on the stack type, default values are:
- build: mvn test, npm run test
- run: mvn spring-boot:run, npm run start
- pack: mvn package, npm run build
# EnvironmentVariables Specification
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | String | Yes | Name of the env variable to inject |
value | String | No | Value to give to the env variable |
secretKeyRef | SecretKeyRef[] | No | A reference to a secret |
# Microservices Environment Variables
The following are platform-provided runtime variables.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
KEYCLOAK_REALM | string | Keycloak or Red Hat Single Sign-On (RH-SSO) realm to be used by the MS. |
KEYCLOAK_AUTH_URL | string | Keycloak/RH-SSO URL to be used by the MS. |
KEYCLOAK_CLIENT_SECRET | secretKeyRef[] | Keycloak/RH-SSO autogenerated clientSecret to be used by the MS. |
KEYCLOAK_CLIENT_ID | secretKeyRef[] | Keycloak/RH-SSO autogenerated clientId to be used by the MS. |
SERVER_SERVLET_CONTEXT_PATH | string | Context path used to access the MS. Automatically handled by a Spring Boot MS, but can be manually set for other stack types. |
SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE | string | Application profile to use when the MS runs on Entando, differentiating dev vs prod at runtime. Automatically handled by a Spring Boot MS but can be manually managed if using another technology stack. |
SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL | string | Provisioned database JDBC connection URL. Automatically handled by a Spring Boot MS but can be manually managed if using another technology stack. |
SPRING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME | string | Provisioned database username. Automatically handled for a Spring Boot MS, but can be manually managed if using another technology stack. |
SPRING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD | string | Provisioned database password. Automatically handled for a Spring Boot MS, but can be manually managed if using another technology stack. |
# Global Specification
| Name | Type | Required | Possible Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
nav | MenuEntry[] | No | Bundle menu global links |
# MenuEntry Specification
| Name | Type | Required | Possible Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
label | String[] | Yes | Localized entry in the PBC menu | |
target | Enum | Yes | *internal *external | Where to open the menu link |
url | String | Address of the page to open when the menu is clicked |
# MfeParam Specification
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | String | Yes | Name of the parameter |
| description | String | No | Description of the parameter |
"params": [
{
"name": "username",
"description": "username of user"
},
{
"name": "description",
"description": "description of user"
}
],
"contextParams": [
"page_code"
]
# Permission Specification
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| clientId | string | Yes | The clientId of the other MS this MS needs access to |
| role | string | Yes | The role required on the OIDC client of the service that the MS needs access to |
# SecretKeyRef Specification
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | String | Yes | The secret name |
key | String | Yes | The secret key inside the secret object |